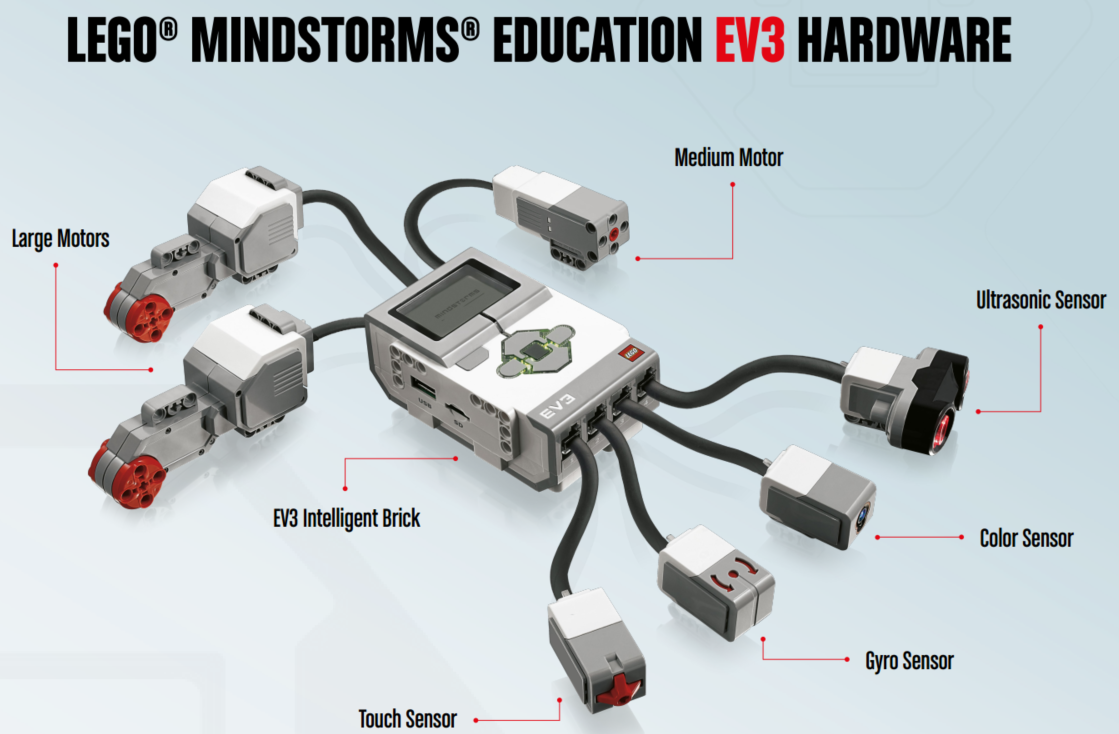
In this class, we will achieve an autonomous parking. Frist, we construct the Robot Educator base model, which is a basic wheeled robot.
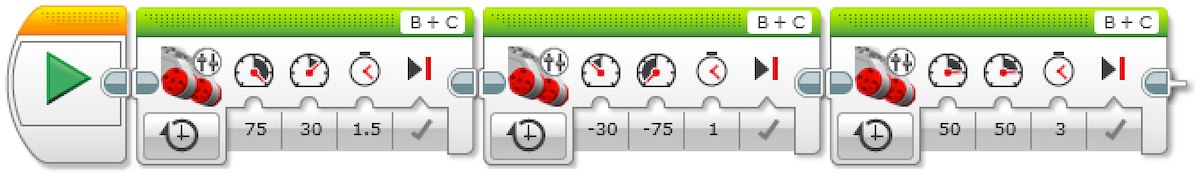
Program 1: Three Point Turn

1. Start the Program
2. Turn the driving base and stop after 1.5 seconds.
3. Turn the driving base left and stop after 1 second.
4. Move the driving base forward for 3 seconds.
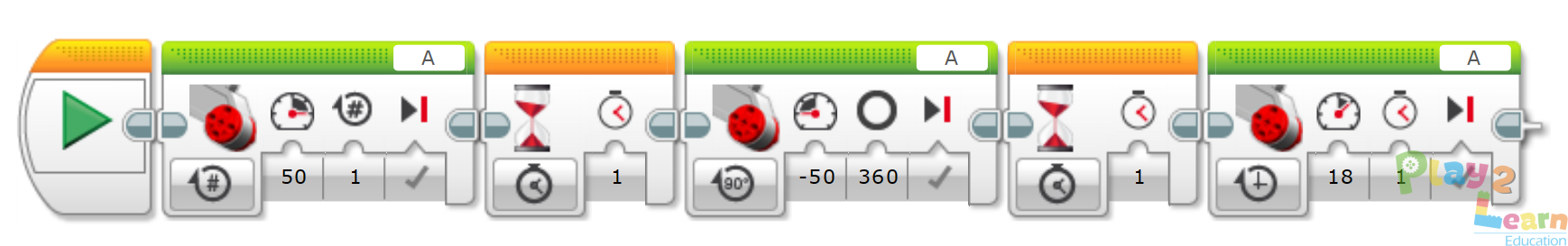
Program 2: Parallel Parking

1. Start the Program.
2. Drive forward in a straight line at the desired speed.
3. Wait for 1 second.
4. Reverse motor rotation while turning for 1.5 rotation.
5. Reverse motor rotation while turning the other way for 1.5 rotation.
6. Drive backward in a straight line for 0.5 rotation.
7. Drive forward in a straight line for 1 rotation.
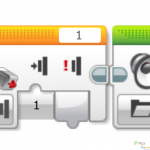
Program 3: Parallel Parking with Simulating Reverse Gear and Reverse Warning lights
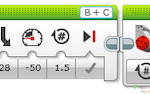
1. Start the Program.
2. Drive forward in a straight line at the desired speed.
3. Wait for 1 second.
4. Turn light on (reverse light).
5. Reverse motor rotation while turning for 1.5 rotation.
6. Reverse motor rotation while turning the other way for 1.5 rotation.
7. Drive backward in a straight line for 0.5 rotation.
8. Drive forward in a straight line for 1 rotation.
After finishing each program, make sure to check the following building before sending command to the wheeled robot: Are the wires correctly connected from the motors to ports B and C? Are the wheels correctly installed? Are the wheels rotating freely?